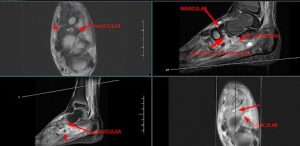
Compressed navicular bone, demonstrate diffuse low intensity with a central ovoid abnormal STIR hyperintensity with internal low intensity rim which is communicating with large surrounding inferior perinavicular collection through a inferior cortical defect – represents osteonecrosis of the navicular bone (Köhler disease ) with secondary osteomyelitis.
Thin fluid collections surrounding the tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus tendons associated with ankle joint effusion – suggestive of infective tenosynovitis.

